Addressing Pakistan's Energy Crisis: Strategic pathways for sustainable solutions

- 228
- 0
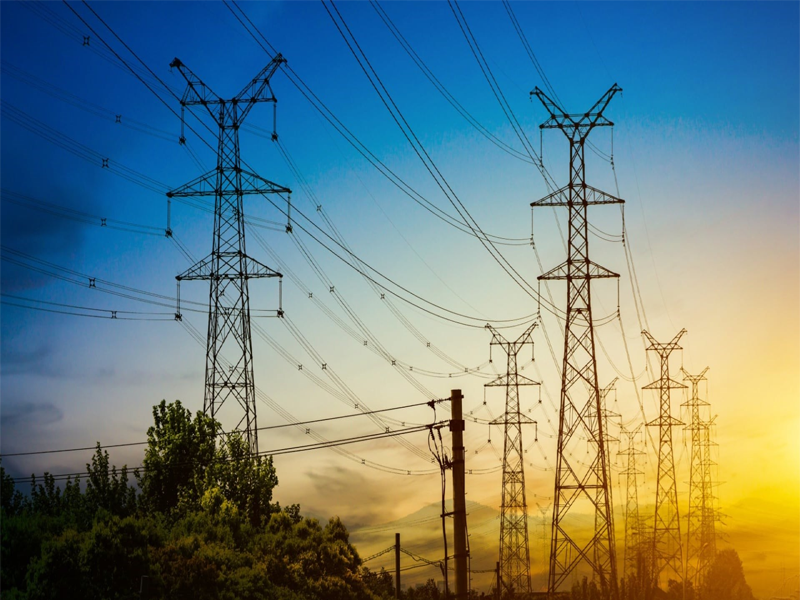
Pakistan's energy crisis has long been a critical issue undermining its economic stability and growth prospects.
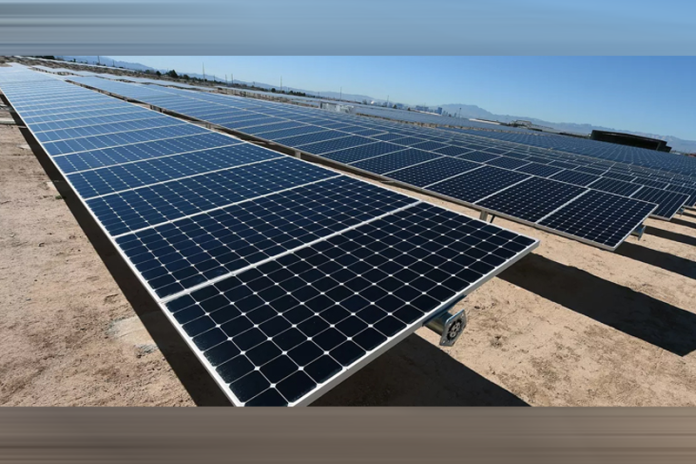
The country faces frequent power shortages, widespread load shedding, and an inefficient energy infrastructure, which hinder industrial productivity and adversely affect daily life. To address these challenges and lift Pakistan from its energy crisis, a multifaceted approach is essential. This article explores key strategies that the Pakistani government can adopt to mitigate the crisis and ensure a more sustainable energy future. 1. Diversifying Energy Sources One of the most pressing needs is to diversify Pakistan's energy mix. Currently, the country heavily relies on fossil fuels, particularly oil and natural gas, which are not only finite but also subject to volatile global markets. Increasing the share of renewable energy sources-such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power-can significantly reduce dependency on fossil fuels. The government should prioritize investment in renewable energy projects by providing incentives for private sector involvement and easing regulatory hurdles. For instance, the implementation of a feed-in tariff system could encourage more investment in solar and wind power by guaranteeing a fixed payment for energy producers.
2. Upgrading Energy Infrastructure Pakistan's existing energy infrastructure is outdated and inefficient. The transmission and distribution networks are plagued with losses due to aging equipment and poor maintenance. Modernizing these networks is crucial for reducing energy wastage and improving overall efficiency. This can be achieved through upgrading transmission lines, enhancing grid management systems, and implementing smart grid technologies. Additionally, the government should focus on improving the maintenance and operation of existing power plants to ensure they run at optimal capacity. 3. Promoting Energy Efficiency Energy efficiency is a cost-effective way to reduce the energy demand and mitigate the crisis.
The government should promote energy-saving practices across various sectors, including residential, commercial, and industrial. Initiatives could include the introduction of energy efficiency standards for appliances and buildings, the promotion of energy-efficient lighting solutions, and the implementation of energy management systems in industries. Public awareness campaigns can also play a vital role in educating citizens about energy conservation practices. 4. Enhancing Governance and Reducing Corruption Corruption and mismanagement have exacerbated Pakistan's energy crisis. Improving governance in the energy sector is crucial for ensuring that resources are utilized effectively and projects are completed on time. The government must enforce strict accountability measures, streamline procurement processes, and enhance transparency in the allocation of energy resources. Establishing independent regulatory bodies with the authority to oversee and audit energy sector operations can help mitigate corruption and ensure that policies are implemented efficiently. 5. Encouraging Private Sector Investment Private sector investment is essential for addressing the energy crisis and developing new energy projects. The government should create a conducive environment for private investment by offering tax incentives, reducing bureaucratic red tape, and ensuring a stable regulatory framework. Public-private partnerships (PPPs) can be particularly effective in developing large-scale energy projects, such as power plants and renewable energy farms. By leveraging private sector expertise and capital, Pakistan can accelerate the development of its energy infrastructure. 6. Exploring Alternative Energy Technologies In addition to traditional renewable energy sources, Pakistan should explore alternative energy technologies such as biomass, geothermal, and tidal power. These technologies have the potential to provide sustainable energy solutions, especially in regions with specific resource availability. For example, biomass energy can be harnessed from agricultural and organic waste, providing both energy and waste management solutions. Investment in research and development of these technologies can position Pakistan as a leader in innovative energy solutions. 7. Strengthening Regional Cooperation Regional cooperation can play a significant role in addressing Pakistan's energy crisis. Collaborating with neighboring countries on cross-border energy projects can enhance energy security and supply stability. For instance, participating in regional energy grids or importing electricity from countries with surplus power can help mitigate supply shortages.
The government should actively engage in regional energy forums and agreements to explore opportunities for cooperation and resource sharing. 8. Investing in Energy Storage Solutions Energy storage technologies are crucial for managing the intermittency of renewable energy sources. Investing in advanced energy storage solutions, such as batteries and pumped hydro storage, can help balance supply and demand by storing excess energy generated during peak production times and releasing it during periods of high demand. The government should support research and development in energy storage technologies and encourage their adoption through subsidies and incentives. 9. Reforming Energy Pricing and Subsidies Energy pricing and subsidy reforms are necessary to ensure that energy resources are allocated efficiently and to encourage energy conservation. The government should gradually phase out subsidies on fossil fuels, which distort market prices and encourage overconsumption. Instead, subsidies can be redirected towards supporting renewable energy projects and improving energy efficiency. Implementing a more transparent and market-driven pricing mechanism can help align energy costs with actual production and distribution expenses.
10. Fostering Innovation and Research Innovation and research are critical for developing new energy solutions and improving existing technologies. The government should support research institutions and universities in exploring cutting-edge energy technologies and solutions. Establishing innovation hubs and research grants can incentivize the development of new energy technologies and attract talent to the sector. Collaboration between academia, industry, and government agencies can drive progress and facilitate the adoption of innovative energy solutions. 11. Developing Human Capital Building a skilled workforce is essential for the growth and development of the energy sector. The government should invest in training and education programs to develop expertise in energy management, engineering, and technology. Partnerships with educational institutions and industry leaders can help align training programs with current industry needs and technological advancements. Developing human capital will ensure that Pakistan has the necessary expertise to drive energy projects and innovations effectively. 12. Improving Public-Private Dialogue Effective communication and collaboration between the public and private sectors are crucial for addressing the energy crisis. The government should establish forums and platforms for regular dialogue with industry stakeholders, including energy producers, consumers, and investors. This collaborative approach can help identify challenges, share best practices, and develop practical solutions. Engaging stakeholders in policy formulation and implementation processes can enhance the effectiveness of energy policies and foster a more cooperative environment. Conclusion Lifting Pakistan from its energy crisis requires a comprehensive and strategic approach that addresses the root causes of the problem while exploring innovative solutions. By diversifying energy sources, upgrading infrastructure, promoting efficiency, and fostering private sector investment, the government can pave the way for a more sustainable and resilient energy sector.
Additionally, strengthening governance, exploring alternative technologies, and investing in human capital will further contribute to overcoming the energy crisis and ensuring long-term energy security for Pakistan. With concerted effort and effective implementation, Pakistan can transform its energy landscape and support its economic growth and development.